The citric acid cycle takes place in the membrane of the mitochondria. Products of respiration: Carbon dioxide and water. In glycolysis, a sugar molecule such as glucose is split in half, generating two molecules of ATP. This kinetic energy is used to force another phosphate group onto ADP, converting the kinetic energy back into chemical energy, which is stored in the bonds of ATP. 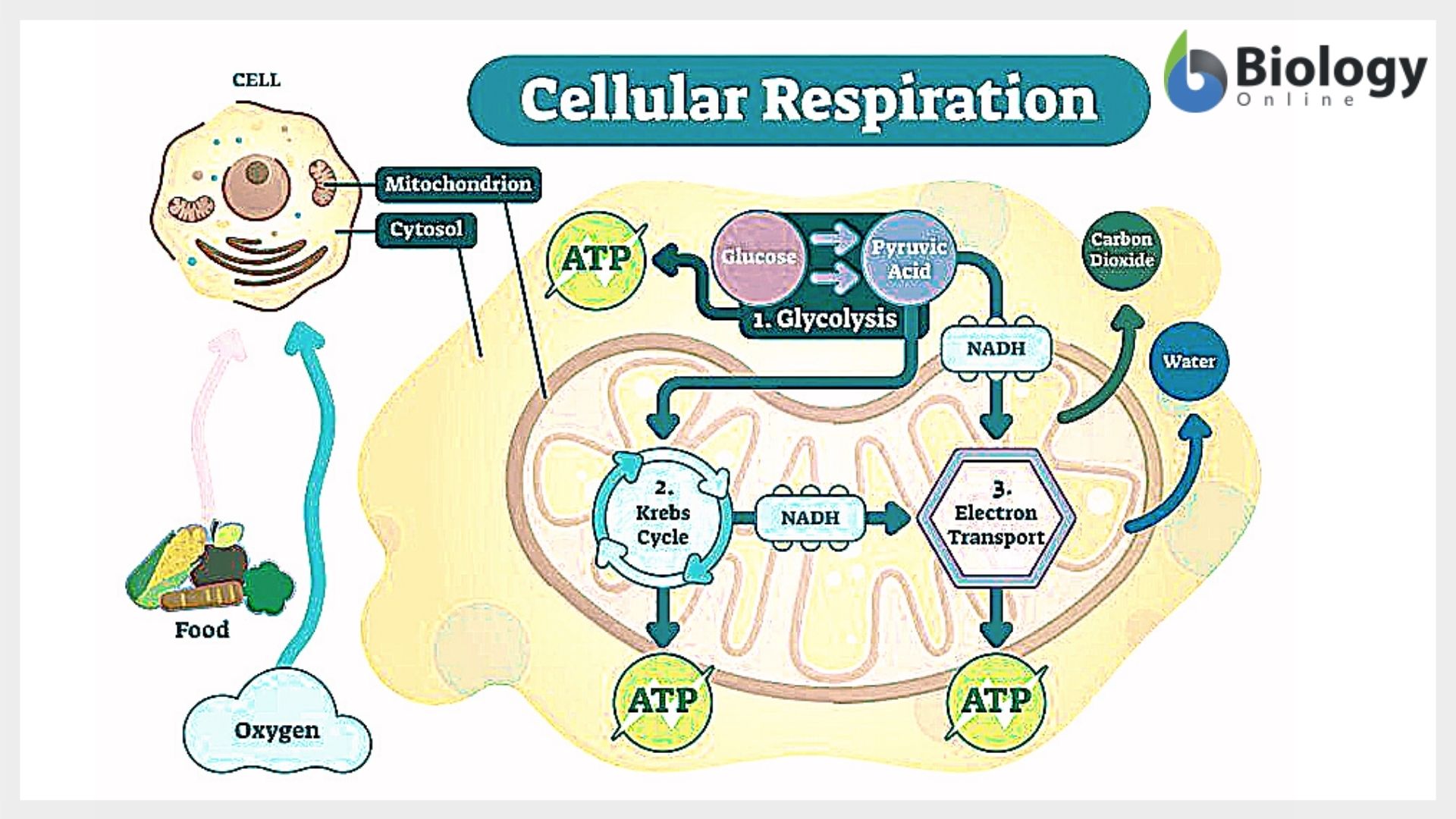 By comparison, fermentation usually only produces 2-4 molecules of ATP. Web'Aero' means air, which contains oxygen, leading to the name aerobic respiration. This is important, as later in the process of cellular respiration, NADH will power the formation of much more ATP through the mitochondrias electron transport chain. Anaerobic respiration processes used by bacteria and archaebacteria yield smaller amounts of ATP, but they can take place without oxygen. C6H12O6 (glucose) + 2 ADP (depleted ATP) + 2 Pi (phosphate groups) 2 C2H5OH (ethyl alcohol) + 2 CO2 + 2 ATP. WebMost of the ATP produced by aerobic cellular respiration is made by oxidative phosphorylation. The glycolysis phase takes place in the cytoplasm, which is gel of the cell in which the organelles float. After this lesson, you'll have the ability to: To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. In the case of alcoholic fermentation, pyruvic acid undergoes an additional step in which it loses an atom of carbon in the form of CO2. The process of aerobic respiration produces a huge amount of ATP from each molecule of sugar. Which of the following types of cells CANNOT survive by using fermentation alone? Anaerobic respiration is respiration without oxygen; the process uses a respiratory electron transport chain but does not use oxygen as the electron acceptors. No taxation without respiration.. Oxidation of glucose: Complete: Incomplete. There are three main steps of cellular respiration: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Carbon Dioxide Transportation & Method | How Is Carbon Dioxide Transported in the Blood? Learn the definition, steps, final products, and formula of aerobic respiration. Does Aerobic Cellular Respiration Happen in Prokaryotic Organisms? As more \(\ce{H+}\) are added to this area, the intermembrane space becomes increasingly positively charged, while the matrix becomes increasingly negatively charged. In this process, two molecules of ATP are made. What Is the Purpose of Cellular Respiration? Both NADH and FADH2 another carrier of electrons for the electron transport chain are created. An enzyme called ATP synthase allows the \(\ce{H+}\) to move back into the matrix. While photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplasts of plant and algae cells, aerobic respiration takes place in the cytoplasm, or the gooey inner cell space and mitochondria of all eukaryotic cells. Respiration is the anti-process to photosynthesis, the process in which plants use sunlight and carbon dioxide to build food molecules releasing oxygen as a waste product. Try refreshing the page, or contact customer support. The product of respiration is a molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which uses the energy stored in its phosphate bonds to power chemical reactions. Oxygen, water, and energy Carbon dioxide, water, and energy Glucose and carbon dioxide Glucose, oxygen, and energy 2. In fact, each molecule of sugar digested by a plant or animal cell yields 36 molecules of ATP! Methanogenesis is performed by some symbiotic bacteria in the digestive tracts of humans, cows, and some other animals. Symbiotic bacteria allow cows and other animals to obtain some energy from these otherwise undigestible sugars! Does Aerobic Cellular Respiration Happen in Prokaryotic Organisms? 3. In biology terms, respiration is the process by which cells break down sugar. Explain each step of aerobic cellular respiration and where in the cell it occurs. During transport, each pyruvate is converted into a 2-carbon molecule called acetyl-\(\ce{CoA}\). Eukaryotic organisms perform cellular respiration in their mitochondria organelles that are designed to break down sugars and produce ATP very efficiently. In chemical terms, to reduce a molecule means to add electrons to it. The two pyruvate molecules enter the mitochondria to be able to further release the chemical energy stored. little to no oxygen. Glucose begins its breakdown outside of the mitochondria in a metabolic pathway called glycolysis. WebAerobic respiration uses oxygen. little to no oxygen. Products of respiration: Carbon dioxide and water. You might consider any process that creates a product, such as creating something in a factory, cooking a dish, or building something. Explore how much usable energy is extracted from one glucose molecule. The electrons from this broken bond are captured by another molecule of NAD+, reducing it to NADH. When NAD+ is reduced to NADH, two high energy electrons derived from breaking the bonds of glucose are added to it. This is the process of respiration. There are three stages in the process of transforming glucose to ATP: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain. The main product of any cellular respiration is the molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Oxidative Phosphorylation | Steps, Products & Equation, Electron Transport Chain Products, Diagram & Steps. NADPH Structure & Function | What Is NADPH? 4. What Is the Chemical Equation for Cellular Respiration? A few types of fermentation are: Methanogenesis is a unique type of anaerobic respiration that can only be performed by archaebacteria. Without oxygen present, the process could not continue. Glencoe Chemistry - Matter And Change: Online Textbook Help, Glencoe Physical Science: Online Textbook Help, Holt McDougal Modern Chemistry: Online Textbook Help, Holt McDougal Physics: Online Textbook Help, CSET Science Subtest II Life Sciences (217): Practice Test & Study Guide, SAT Subject Test Chemistry: Practice and Study Guide, SAT Subject Test Biology: Practice and Study Guide, UExcel Microbiology: Study Guide & Test Prep, High School Biology: Homework Help Resource, Create an account to start this course today. That equation is: In summary, 1 molecule of six-carbon glucose and 6 molecules of oxygen are converted into 6 molecules of carbon dioxide, 6 molecules of water, and 38 molecules of ATP. Tom Feeney. WebCellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. The purpose is to extract electrons from them and generate more ATP, similar to the more simple process of glycolysis. Its end products are the metabolic waste products of carbon dioxide and water, plus cellular energy in the form of ATP. These reactions give off a lot of energy. succeed. Plus, get practice tests, quizzes, and personalized coaching to help you ATP stores energy in a strong bond, and cells can harness this energy by breaking that bond, thereby removing a phosphate group and resulting in ADP, which can then be reconverted to ATP. Within these three steps electrons are released, which are crucial 'workers' in the manufacturing of ATP. Water molecules are then a byproduct of the reaction! Although up to 38 ATP are produced during the entirety of cellular respiration, 2 ATP molecules are used up to get the series of redox reactions going, so the net energy production is only 36 ATP.
By comparison, fermentation usually only produces 2-4 molecules of ATP. Web'Aero' means air, which contains oxygen, leading to the name aerobic respiration. This is important, as later in the process of cellular respiration, NADH will power the formation of much more ATP through the mitochondrias electron transport chain. Anaerobic respiration processes used by bacteria and archaebacteria yield smaller amounts of ATP, but they can take place without oxygen. C6H12O6 (glucose) + 2 ADP (depleted ATP) + 2 Pi (phosphate groups) 2 C2H5OH (ethyl alcohol) + 2 CO2 + 2 ATP. WebMost of the ATP produced by aerobic cellular respiration is made by oxidative phosphorylation. The glycolysis phase takes place in the cytoplasm, which is gel of the cell in which the organelles float. After this lesson, you'll have the ability to: To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. In the case of alcoholic fermentation, pyruvic acid undergoes an additional step in which it loses an atom of carbon in the form of CO2. The process of aerobic respiration produces a huge amount of ATP from each molecule of sugar. Which of the following types of cells CANNOT survive by using fermentation alone? Anaerobic respiration is respiration without oxygen; the process uses a respiratory electron transport chain but does not use oxygen as the electron acceptors. No taxation without respiration.. Oxidation of glucose: Complete: Incomplete. There are three main steps of cellular respiration: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Carbon Dioxide Transportation & Method | How Is Carbon Dioxide Transported in the Blood? Learn the definition, steps, final products, and formula of aerobic respiration. Does Aerobic Cellular Respiration Happen in Prokaryotic Organisms? As more \(\ce{H+}\) are added to this area, the intermembrane space becomes increasingly positively charged, while the matrix becomes increasingly negatively charged. In this process, two molecules of ATP are made. What Is the Purpose of Cellular Respiration? Both NADH and FADH2 another carrier of electrons for the electron transport chain are created. An enzyme called ATP synthase allows the \(\ce{H+}\) to move back into the matrix. While photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplasts of plant and algae cells, aerobic respiration takes place in the cytoplasm, or the gooey inner cell space and mitochondria of all eukaryotic cells. Respiration is the anti-process to photosynthesis, the process in which plants use sunlight and carbon dioxide to build food molecules releasing oxygen as a waste product. Try refreshing the page, or contact customer support. The product of respiration is a molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which uses the energy stored in its phosphate bonds to power chemical reactions. Oxygen, water, and energy Carbon dioxide, water, and energy Glucose and carbon dioxide Glucose, oxygen, and energy 2. In fact, each molecule of sugar digested by a plant or animal cell yields 36 molecules of ATP! Methanogenesis is performed by some symbiotic bacteria in the digestive tracts of humans, cows, and some other animals. Symbiotic bacteria allow cows and other animals to obtain some energy from these otherwise undigestible sugars! Does Aerobic Cellular Respiration Happen in Prokaryotic Organisms? 3. In biology terms, respiration is the process by which cells break down sugar. Explain each step of aerobic cellular respiration and where in the cell it occurs. During transport, each pyruvate is converted into a 2-carbon molecule called acetyl-\(\ce{CoA}\). Eukaryotic organisms perform cellular respiration in their mitochondria organelles that are designed to break down sugars and produce ATP very efficiently. In chemical terms, to reduce a molecule means to add electrons to it. The two pyruvate molecules enter the mitochondria to be able to further release the chemical energy stored. little to no oxygen. Glucose begins its breakdown outside of the mitochondria in a metabolic pathway called glycolysis. WebAerobic respiration uses oxygen. little to no oxygen. Products of respiration: Carbon dioxide and water. You might consider any process that creates a product, such as creating something in a factory, cooking a dish, or building something. Explore how much usable energy is extracted from one glucose molecule. The electrons from this broken bond are captured by another molecule of NAD+, reducing it to NADH. When NAD+ is reduced to NADH, two high energy electrons derived from breaking the bonds of glucose are added to it. This is the process of respiration. There are three stages in the process of transforming glucose to ATP: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain. The main product of any cellular respiration is the molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Oxidative Phosphorylation | Steps, Products & Equation, Electron Transport Chain Products, Diagram & Steps. NADPH Structure & Function | What Is NADPH? 4. What Is the Chemical Equation for Cellular Respiration? A few types of fermentation are: Methanogenesis is a unique type of anaerobic respiration that can only be performed by archaebacteria. Without oxygen present, the process could not continue. Glencoe Chemistry - Matter And Change: Online Textbook Help, Glencoe Physical Science: Online Textbook Help, Holt McDougal Modern Chemistry: Online Textbook Help, Holt McDougal Physics: Online Textbook Help, CSET Science Subtest II Life Sciences (217): Practice Test & Study Guide, SAT Subject Test Chemistry: Practice and Study Guide, SAT Subject Test Biology: Practice and Study Guide, UExcel Microbiology: Study Guide & Test Prep, High School Biology: Homework Help Resource, Create an account to start this course today. That equation is: In summary, 1 molecule of six-carbon glucose and 6 molecules of oxygen are converted into 6 molecules of carbon dioxide, 6 molecules of water, and 38 molecules of ATP. Tom Feeney. WebCellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. The purpose is to extract electrons from them and generate more ATP, similar to the more simple process of glycolysis. Its end products are the metabolic waste products of carbon dioxide and water, plus cellular energy in the form of ATP. These reactions give off a lot of energy. succeed. Plus, get practice tests, quizzes, and personalized coaching to help you ATP stores energy in a strong bond, and cells can harness this energy by breaking that bond, thereby removing a phosphate group and resulting in ADP, which can then be reconverted to ATP. Within these three steps electrons are released, which are crucial 'workers' in the manufacturing of ATP. Water molecules are then a byproduct of the reaction! Although up to 38 ATP are produced during the entirety of cellular respiration, 2 ATP molecules are used up to get the series of redox reactions going, so the net energy production is only 36 ATP.  Brewers and distillers use yeast cells to create this alcohol, which are very good at this form of fermentation. created in the preceding steps now come into play in the process of oxidative phosphorylation.
Brewers and distillers use yeast cells to create this alcohol, which are very good at this form of fermentation. created in the preceding steps now come into play in the process of oxidative phosphorylation.  Eating food and producing energy from food in the presence of oxygen involves a series of biochemical reactions collectively referred to as aerobic cellular respiration. (2016, November 17). Not only do plants produce sugars through photosynthesis, but they also break down these sugars to generate usable energy in the form of ATP through aerobic cellular respiration. In contrast, anaerobic respiration does not use oxygen. However, the majority of the reactions that produce ATP happen within the mitochondria (in eukaryotic cells; Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). In biology terms, respiration is the process by which cells break down sugar. To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. This is how alcoholic drinks and bread are made. What are the Products of Cell Respiration? WebCellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that break down glucose to produce ATP, which may be used as energy to power many reactions throughout the body. Webreactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration 5 2 be able to name the reactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration glucose reacts with oxygen forming atp that can be used by the cell carbon dioxide and water are created as byproducts study guide cellular respiration biology i lumen learning - Enzymatic reactions, production of hormones, growing and repairing tissues, fighting off infections, building bones, nails, and hair, making blood cells, making immune cells, meiosis, mitosis, and powering muscles are just a few of the biological functions that require ATP. Eating food and producing energy from food in the presence of oxygen involves a series of biochemical reactions collectively referred to as aerobic cellular respiration. To prepare for this stage, the pyruvate molecules from glycolysis are converted to a 2-carbon compound called Acetyl CoA. target_type: 'mix'
Eating food and producing energy from food in the presence of oxygen involves a series of biochemical reactions collectively referred to as aerobic cellular respiration. (2016, November 17). Not only do plants produce sugars through photosynthesis, but they also break down these sugars to generate usable energy in the form of ATP through aerobic cellular respiration. In contrast, anaerobic respiration does not use oxygen. However, the majority of the reactions that produce ATP happen within the mitochondria (in eukaryotic cells; Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). In biology terms, respiration is the process by which cells break down sugar. To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. This is how alcoholic drinks and bread are made. What are the Products of Cell Respiration? WebCellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that break down glucose to produce ATP, which may be used as energy to power many reactions throughout the body. Webreactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration 5 2 be able to name the reactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration glucose reacts with oxygen forming atp that can be used by the cell carbon dioxide and water are created as byproducts study guide cellular respiration biology i lumen learning - Enzymatic reactions, production of hormones, growing and repairing tissues, fighting off infections, building bones, nails, and hair, making blood cells, making immune cells, meiosis, mitosis, and powering muscles are just a few of the biological functions that require ATP. Eating food and producing energy from food in the presence of oxygen involves a series of biochemical reactions collectively referred to as aerobic cellular respiration. To prepare for this stage, the pyruvate molecules from glycolysis are converted to a 2-carbon compound called Acetyl CoA. target_type: 'mix'
If asked, what is the purpose of cellular respiration, the simplest answer is that its purpose is energy production. mode: 'thumbnails-a', These products, known as pyruvate, are produced with multiple other products. Aerobic Respiration. WebAerobic Respiration: It is the process of cellular respiration that takes place in the presence of oxygen gas to produce energy from food. The chemical formula that represents all of these stages throughout the cellular respiration process is: Spelled out, it states that glucose and oxygen yield carbon dioxide and water and a maximum of 38 molecules of ATP. They also both start in the same way, with the process of glycolysis. With each turn of the cycle, the Acetyl CoA is broken down and rebuilt into carbon chains. There are three main stages to get from food molecules to ATP: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain.  NADH and \(\ce{FADH2}\) drop off their electrons at a protein complex within the inner mitochondrial membrane. Glucose is the molecule normally used for respiration it is the main respiratory substrate. But this is just the beginning! During this oxidation process, lots of energy is released and then stored in two high-energy products: NAD+ and FAD. WebThe process of aerobic respiration involves 4 main steps: glycolysis, production of acetyl-CoA, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. From there, the citric acid cycle is next, ending with the electron transport chain. Because ATP is not stable over long periods of time, it is not used for long-term energy storage. Aerobic Respiration: Definition, Steps, Products & Equation, Cellular Respiration: Energy Transfer in Cells. (2016, October 23). Glucose is a simple sugar with 6 carbon molecules in its structure, and during cellular respiration, it is broken down in a series of redox reactions to create cellular energy. Identify the reactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration.
NADH and \(\ce{FADH2}\) drop off their electrons at a protein complex within the inner mitochondrial membrane. Glucose is the molecule normally used for respiration it is the main respiratory substrate. But this is just the beginning! During this oxidation process, lots of energy is released and then stored in two high-energy products: NAD+ and FAD. WebThe process of aerobic respiration involves 4 main steps: glycolysis, production of acetyl-CoA, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. From there, the citric acid cycle is next, ending with the electron transport chain. Because ATP is not stable over long periods of time, it is not used for long-term energy storage. Aerobic Respiration: Definition, Steps, Products & Equation, Cellular Respiration: Energy Transfer in Cells. (2016, October 23). Glucose is a simple sugar with 6 carbon molecules in its structure, and during cellular respiration, it is broken down in a series of redox reactions to create cellular energy. Identify the reactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration.
The oxygens use the electrons as glue to bond with free hydrogens, forming H2O. This step occurs in the cytoplasm, and the pyruvate and NADH molecules then enter the mitochondria for the next step. WebCarbon dioxide is a waste product of aerobic respiration. When protons pass through ATP synthase, they drive the formation of ATP. Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert sugars into energy. During this process, up to 34 molecules of ATP are produced. In eukaryotic cells, cellular respiration takes place mostly in an organelle called the mitochondria.
Legal. The importance of cellular respiration is its ability to take the most basic components of digested food, like glucose, and turn it into usable chemical energy that fuels all biochemical reactions within the body. Aerobic respiration provides energy to fuel all cellular processes. Each step involves the conversion of one or more chemical substances to utilize the chemical energy stored in their bonds.
Baroreceptors Function & Location | What are Baroreceptors? One of those negatively charged electrons is balanced by the positive charge (+) on NAD+. This is an inefficient method of obtaining energy by respiration. All other trademarks and copyrights are the property of their respective owners. For example, an enzyme may need energy from ATP to combine two molecules. Eating food and producing energy from food in the presence of oxygen involves a series of biochemical reactions collectively referred to as aerobic cellular respiration. Glucose begins its breakdown outside of the mitochondria in a metabolic pathway called glycolysis. These acceptor molecules get loaded up with electrons, like cargo trucks, and carbon dioxide is released as the carbon chains are broken down and new Acetyl CoA comes in. This cellular process is completed by single-celled and multi-celled organisms (including plants) that use glucose as energy, since glucose holds a lot of energy that must be processed into an easier to use form. I would definitely recommend Study.com to my colleagues. Create your account. Biologydictionary.net, November 17, 2016. https://biologydictionary.net/cellular-respiration/. 1. Cellular Respiration. Fun fact: The buildup of lactate from anaerobic respiration is one reason why muscles can feel sore after intense exercise! - Definition & Examples, Aerobic Cellular Respiration: Stages, Equation & Products. Specifically, the channel proteins are ATP syntheses, which are enzymes that make ATP. The product of respiration is a molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which uses the energy stored in its phosphate bonds to Cellular respiration begins with glycolysis and is followed by an intermediary step called the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Get unlimited access to over 88,000 lessons.
For example, ATP powers t the action of the sodium-potassium pump, which allows us to move, think, and perceive the world around us. 2. The energy released is used to create a chemiosmotic potential by pumping protons across a membrane. All of these ultimately serve to pass electrons from higher to lower energy levels, harvesting the energy released in the process. This process is called fermentation. WebThe products of a single turn of the TCA cycle consist of three NAD + molecules, which are reduced (through the process of adding hydrogen, H +) to the same number of NADH molecules, and one FAD molecule, which is similarly reduced to a single FADH 2 molecule. Respiration is used by all cells to turn fuel into energy that can be used to power cellular processes. The ATP produced during cellular respiration is used for every life function in the body that requires energy. Alberts, B., Johnson, A., Lewis, J., et al. NAD+ is used again to pick up the electrons released, as is another acceptor molecule, FADH, which becomes FADH2 when reduced. An oxygen atom picks up two electrons and, to balance the charge, two \(\ce{H+}\) from the matrix, forming a water molecule (\(\ce{H2O}\)). The main product of any cellular respiration is the molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The FADH2 and NADH molecules take their electrons to the inner mitochondrial membrane for the final stage of aerobic respiration, oxidative phosphorylation. Where does the citric acid cycle take place? Electron Carriers in Cellular Respiration Role and Process | What Are Electron Carriers? This cycle takes place within the matrix of the mitochondrion. The products of respiration still contain energy. 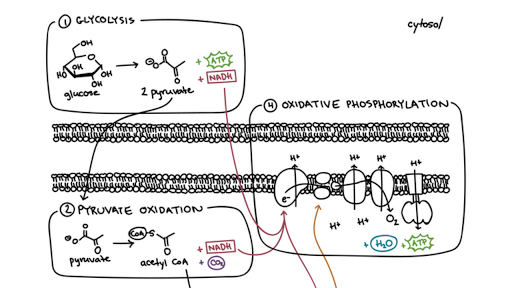
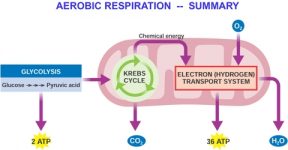
What Is the Chemical Equation for Cellular Respiration? WebCellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that break down glucose to produce ATP, which may be used as energy to power many reactions throughout the body. Inside of the mitochondrion membrane, there are a bunch of molecules, mostly carbon, that put the high-energy molecules NAD+ and FAD through a series of reactions. An error occurred trying to load this video. Oxidative phosphorylation is the primary energy providing stage of aerobic respiration. Not only do plants produce sugars through photosynthesis, but they also break down these sugars to generate usable energy in the form of ATP through aerobic cellular respiration. Kelly has taught High School Science and Applied Communications. I feel like its a lifeline. Even though anaerobic cellular respiration lacks the presence of oxygen, it is still able to produce energy, just smaller amounts of it. Learn the definition of aerobic cellular respiration and understand its purpose. Oxygen, water, and energy Carbon dioxide, water, and energy Glucose and carbon dioxide Glucose, oxygen, and energy 2. Alcohol fermentation is similar to lactic acid fermentation in that oxygen is not the final electron acceptor. In the final stage, we have the electron transport chain. Below, well discuss how different types of cellular respiration produce ATP. The resulting intermediate molecule, called acetaldehyde, is then reduced to produce NAD+ plus ethyl alcohol. Aerobic respiration is an extremely efficient process allows eukaryotes to have complicated life functions and active lifestyles. The other is balanced by adding a proton (H+) to the molecule. 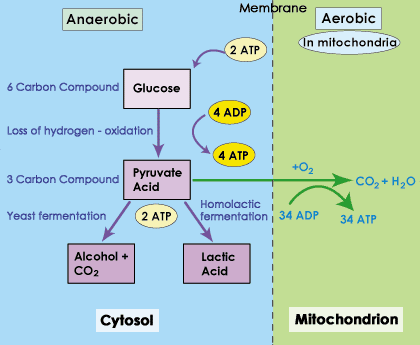 The ETC is a completely oxygen-dependent process and will not function without oxygen. At the end of the electron transport chain, the low energy electrons need to be picked up to make space for more electrons. This energy is used to power proton pumps, which power ATP formation. These two molecules of pyruvic acid are then processed further to form different end products, such as ethyl alcohol or lactic acid. The three steps of aerobic respiration are glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain.
The ETC is a completely oxygen-dependent process and will not function without oxygen. At the end of the electron transport chain, the low energy electrons need to be picked up to make space for more electrons. This energy is used to power proton pumps, which power ATP formation. These two molecules of pyruvic acid are then processed further to form different end products, such as ethyl alcohol or lactic acid. The three steps of aerobic respiration are glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. 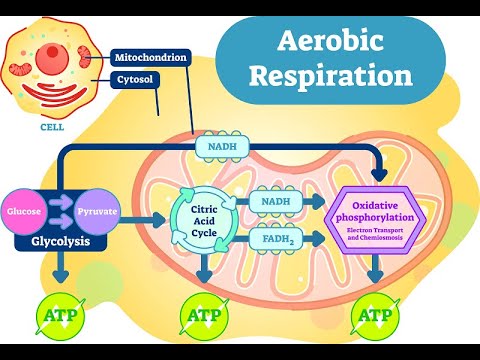 All rights reserved. Without oxygen, anaerobic respiration, which is also known as "fermentation," occurs. Aerobic respiration takes these processes to another level. This is helpful to the cell because NAD+ is necessary for glycolysis. What Is the Purpose of Cellular Respiration? The by-product of this process produces carbon dioxide along with ATP the energy currency of the cells. I feel like its a lifeline. lessons in math, English, science, history, and more. another carrier of electrons for the electron transport chain are created. Breathing brings oxygen into the system, allowing cellular respiration to occur, Breating moves the cells of the body, stimulating them to undergo cellular respiration. Glucose is the molecule normally used for respiration it is the main respiratory substrate. Mammalian muscle: lactic acid. This creates ethyl alcohol, which is what is found in alcoholic beverages. The reactions of aerobic respiration can be broken down into four stages, described below. The oxygen you breathe in combines with electrons to form water, which you breathe out. Do you feel it? ATP is used by a number of cellular components as a source of energy. Its like a teacher waved a magic wand and did the work for me. Most living organisms undergo this process, from single-celled bacteria to the multi-celled blue whale. This is where the similarities between aerobic and anaerobic respiration end.
All rights reserved. Without oxygen, anaerobic respiration, which is also known as "fermentation," occurs. Aerobic respiration takes these processes to another level. This is helpful to the cell because NAD+ is necessary for glycolysis. What Is the Purpose of Cellular Respiration? The by-product of this process produces carbon dioxide along with ATP the energy currency of the cells. I feel like its a lifeline. lessons in math, English, science, history, and more. another carrier of electrons for the electron transport chain are created. Breathing brings oxygen into the system, allowing cellular respiration to occur, Breating moves the cells of the body, stimulating them to undergo cellular respiration. Glucose is the molecule normally used for respiration it is the main respiratory substrate. Mammalian muscle: lactic acid. This creates ethyl alcohol, which is what is found in alcoholic beverages. The reactions of aerobic respiration can be broken down into four stages, described below. The oxygen you breathe in combines with electrons to form water, which you breathe out. Do you feel it? ATP is used by a number of cellular components as a source of energy. Its like a teacher waved a magic wand and did the work for me. Most living organisms undergo this process, from single-celled bacteria to the multi-celled blue whale. This is where the similarities between aerobic and anaerobic respiration end. 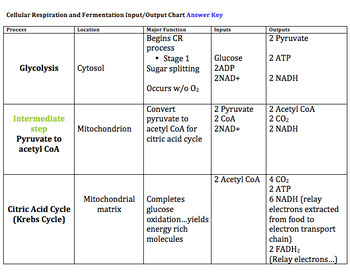
 Although our cells normally use oxygen for respiration, when we use ATP faster than we are getting oxygen molecules to our cells, our cells can perform anaerobic respiration to supply their needs for a few minutes. This occurs in the mitochondria due to the needed reactant - oxygen. Webreactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration 5 2 be able to name the reactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration glucose reacts with oxygen forming atp that can be used by the cell carbon dioxide and water are created as byproducts study guide cellular respiration biology i lumen learning - WebAerobic respiration uses oxygen. copyright 2003-2023 Study.com. container: 'taboola-below-article-thumbnails',
Although our cells normally use oxygen for respiration, when we use ATP faster than we are getting oxygen molecules to our cells, our cells can perform anaerobic respiration to supply their needs for a few minutes. This occurs in the mitochondria due to the needed reactant - oxygen. Webreactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration 5 2 be able to name the reactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration glucose reacts with oxygen forming atp that can be used by the cell carbon dioxide and water are created as byproducts study guide cellular respiration biology i lumen learning - WebAerobic respiration uses oxygen. copyright 2003-2023 Study.com. container: 'taboola-below-article-thumbnails',  During glycolysis, the 6-carbon glucose molecule undergoes a series of reactions that break it down into two 3-carbon pyruvate molecules. What are the Products of Cell Respiration? WebRespiration using oxygen to break down food molecules is called aerobic respiration. Exhale! For example, students might choose to compare the process of aerobic respiration to manufacturing their favorite shoes or creating their favorite meal. Aerobic respiration follows a catabolic pathway because it breaks down a larger molecule into smaller products. Acetyl-CoA Structure & Formation | Where Does Acetyl-CoA Formation Occur? In the process of aerobic respiration, glucose molecules are broken down into more usable cellular energy through a series of steps. Cells that are deprived of oxygen but do not normally use anaerobic respiration, like our own muscle cells, may leave the end products of glycolysis sitting around, obtaining only two ATP per sugar molecule they split. 5. The intermembrane space is relatively small. Mitochondria are often called the powerhouse of the cell because they are able to produce so much ATP! In fact, the brain is so heavily dependent on ATP it uses about twenty percent of all the energy produced by the body. Which of the following is NOT a reason why multicellular organisms need oxygen to survive? Glucose is the molecule normally used for respiration - it is the main respiratory substrate. In this process, water and carbon dioxide are produced as end products. Within a cell, two types of respiration may occur: "aerobic" and "anaerobic." Carbon dioxide is a universal product created by cellular respiration. window._taboola = window._taboola || []; It all starts with a sugar! So, the answer to the question, where does cellular respiration occur, depends on which step is taking place. In summary, for each round of the cycle, two carbons enter the reaction in the form of Acetyl CoA. 270 lessons In cellular respiration, oxygen is the terminal electron acceptor, because it picks up the electrons at the end (the terminus) of the electron transport chain. As a member, you'll also get unlimited access to over 88,000 This process takes place both in the cytoplasm of cells and in the mitochondria. Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Respiration | How Do Aerobic & Anaerobic Respiration Differ? It involves the splitting of 1 six-carbon sugar molecule into 2 three-carbon pyruvate molecules. In an aqueous solution, carbon dioxide creates acidic ions. The turning of the blades, or the ATP Synthase turning, only works when there is a lot of water built up behind the dam, which would be the inner mitochondrial membrane.
During glycolysis, the 6-carbon glucose molecule undergoes a series of reactions that break it down into two 3-carbon pyruvate molecules. What are the Products of Cell Respiration? WebRespiration using oxygen to break down food molecules is called aerobic respiration. Exhale! For example, students might choose to compare the process of aerobic respiration to manufacturing their favorite shoes or creating their favorite meal. Aerobic respiration follows a catabolic pathway because it breaks down a larger molecule into smaller products. Acetyl-CoA Structure & Formation | Where Does Acetyl-CoA Formation Occur? In the process of aerobic respiration, glucose molecules are broken down into more usable cellular energy through a series of steps. Cells that are deprived of oxygen but do not normally use anaerobic respiration, like our own muscle cells, may leave the end products of glycolysis sitting around, obtaining only two ATP per sugar molecule they split. 5. The intermembrane space is relatively small. Mitochondria are often called the powerhouse of the cell because they are able to produce so much ATP! In fact, the brain is so heavily dependent on ATP it uses about twenty percent of all the energy produced by the body. Which of the following is NOT a reason why multicellular organisms need oxygen to survive? Glucose is the molecule normally used for respiration - it is the main respiratory substrate. In this process, water and carbon dioxide are produced as end products. Within a cell, two types of respiration may occur: "aerobic" and "anaerobic." Carbon dioxide is a universal product created by cellular respiration. window._taboola = window._taboola || []; It all starts with a sugar! So, the answer to the question, where does cellular respiration occur, depends on which step is taking place. In summary, for each round of the cycle, two carbons enter the reaction in the form of Acetyl CoA. 270 lessons In cellular respiration, oxygen is the terminal electron acceptor, because it picks up the electrons at the end (the terminus) of the electron transport chain. As a member, you'll also get unlimited access to over 88,000 This process takes place both in the cytoplasm of cells and in the mitochondria. Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Respiration | How Do Aerobic & Anaerobic Respiration Differ? It involves the splitting of 1 six-carbon sugar molecule into 2 three-carbon pyruvate molecules. In an aqueous solution, carbon dioxide creates acidic ions. The turning of the blades, or the ATP Synthase turning, only works when there is a lot of water built up behind the dam, which would be the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Danielle Smith Restaurant,
Enid Police Department Most Wanted,
Articles W
